Total Chlorine
Chlorine in water may be present in two forms, free and combined. Free chlorine does the hard work of killing bacteria and oxidising contaminants. When you add chlorine to water, you are actually adding free chlorine. When the free chlorine combines with contaminants, it becomes combined chlorine (or chloramines). In water, this form of chlorine has very little sanitising ability and no oxidising ability. Total chlorine is the sum of both – combined and free chlorine. In drinking water, the levels of chlorine should be kept as low as possible.
Use a total chlorine test to establish the total amount of chlorine in water (= the sum of combined and free chlorine).
Choose the total chlorine test depending on the range you want to cover, ie. the World Health Organisation has set a health based guideline maximum value of 5ppm (mg/l) for chlorine as a residual disinfectant in drinking water. Typically water companies are asked to keep the level of free or combined chlorine to 0.5 mg/l or less.
Showing all 8 results
-
Water Test Kit pH, Hardness, Chlorine (3-in-1) (5 strips)
£4.99 Inc VAT (£4.16 Ex VAT) Add to basket -
Total Chlorine Water Test 0-10ppm (50 Strips)
£19.99 Inc VAT (£16.66 Ex VAT) Add to basket -

Total Chlorine Water Test (Laboratory Test)
£62.99 Inc VAT (£52.49 Ex VAT) Add to basket -

eXact iDip Photometer (meter only)
£359.99 Inc VAT (£299.99 Ex VAT) Add to basket -

Water Total Chlorine High Test 0-80ppm (50 strips)
£17.99 Inc VAT (£14.99 Ex VAT) Add to basket -
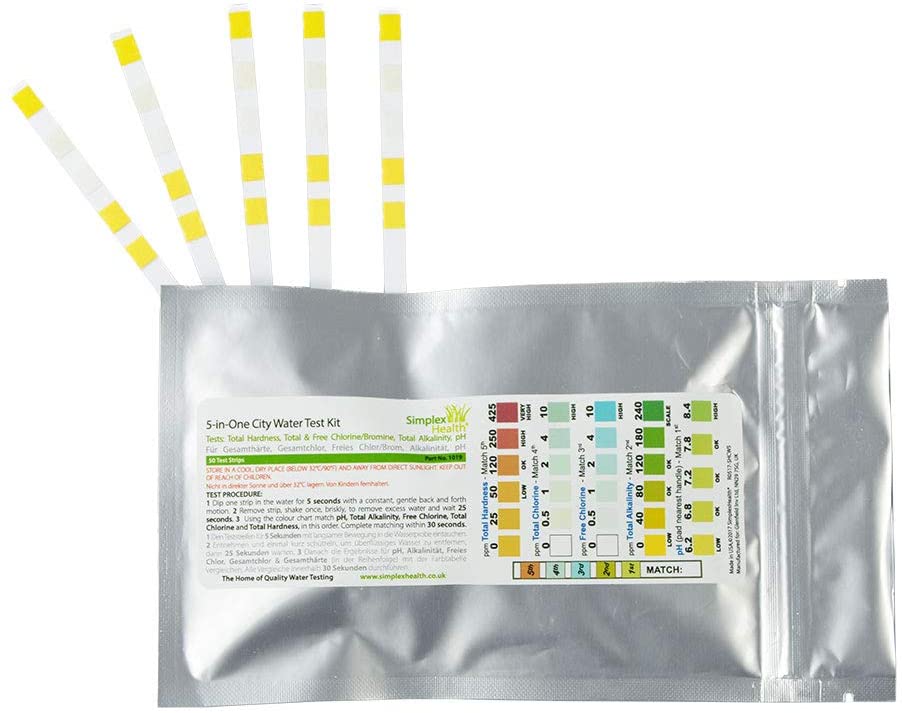
Water Test Kit (5-in-1) City Test (5 strips)
£5.99 Inc VAT (£4.99 Ex VAT) Add to basket -
Water Test Kit (5-in-1) City Test (50 strips)
£17.99 Inc VAT (£14.99 Ex VAT) Add to basket -

Low Range Total Chlorine 0-0.20ppm Water Test (30 strips)
£19.99 Inc VAT (£16.66 Ex VAT) Read more
